RainLink Workflow
Cross-chain bridge technology enables asset transfers between different blockchains. Below is an in-depth look at its core components and workflow.
Key Components
A cross-chain bridge consists of three main parts:
Custodian
- Locks the user’s deposited assets.
- Deployed on the source chain (e.g., Ethereum) via a smart contract.
Debt Issuer
- Mints corresponding tokens on the target chain.
- Implemented on the target chain as a smart contract.
Communicator
- Relays messages between chains.
- Runs off-chain, continuously monitoring source-chain events and forwarding them to the target chain.
Workflow
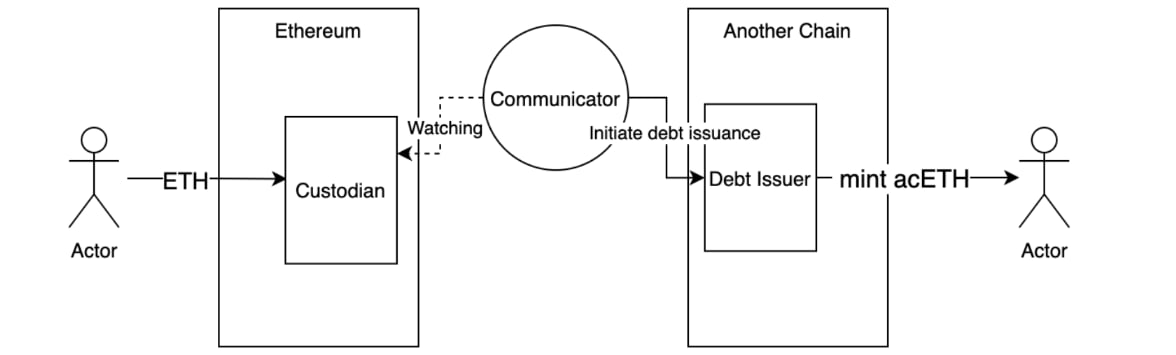
- The user invokes a contract call to deposit ETH into the custodian on Ethereum.
- The custodian smart contract emits an event confirming receipt.
- The communicator detects this event and sends a signal to the debt issuer on the target chain.
- The debt issuer mints the wrapped token (
acETH) and transfers it to the user’s address, completing the cross-chain transfer.
To reverse the process:
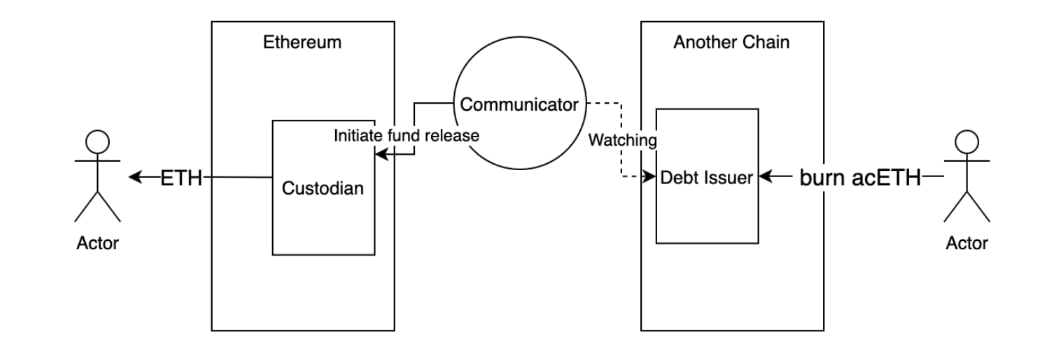
- The user burns
acETHvia the debt issuer on the target chain. - Once the burn is confirmed, the debt issuer emits a redemption event.
- The communicator picks up this event and notifies the custodian on the source chain.
- The custodian releases the original ETH back to the user’s address.
Fees & Security Checks
When bridging assets, two factors are crucial: fees and validity verification.
Fees
Users typically pay:
-
Transaction Fee: Gas costs on the source and/or target blockchain (e.g., Ethereum gas).
-
Service Fee: Charged by the bridge provider. See Bridge Fee Schedule for details.
Validity Verification
The communicator ensures security by:
-
Executing the lock or burn on the source chain.
-
Waiting for a sufficient number of confirmations to guarantee finality.
-
Relaying the event only after confirmation, ensuring the cross-chain transfer is both safe and valid.
Last updated on